Frederick Clayton and Sonja Smith
Photography by Margaret Courtney-Clarke
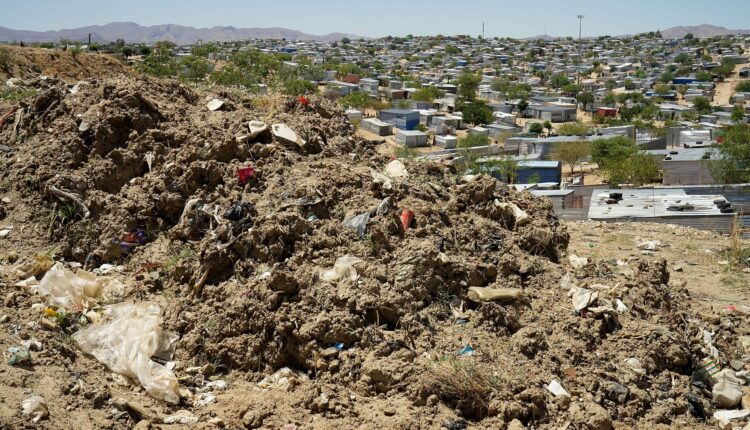
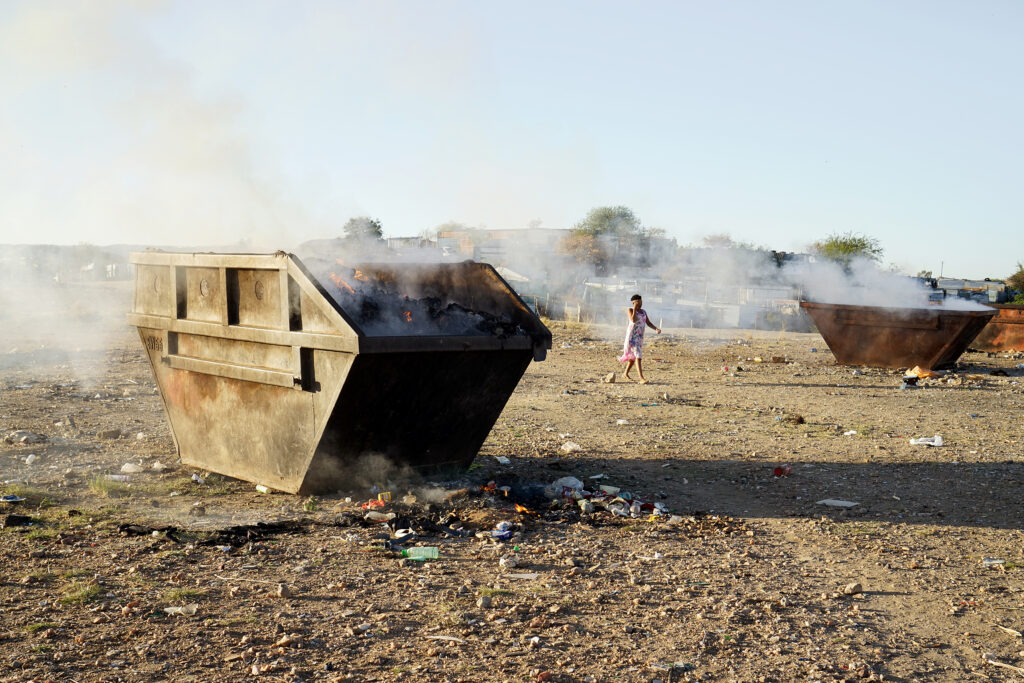
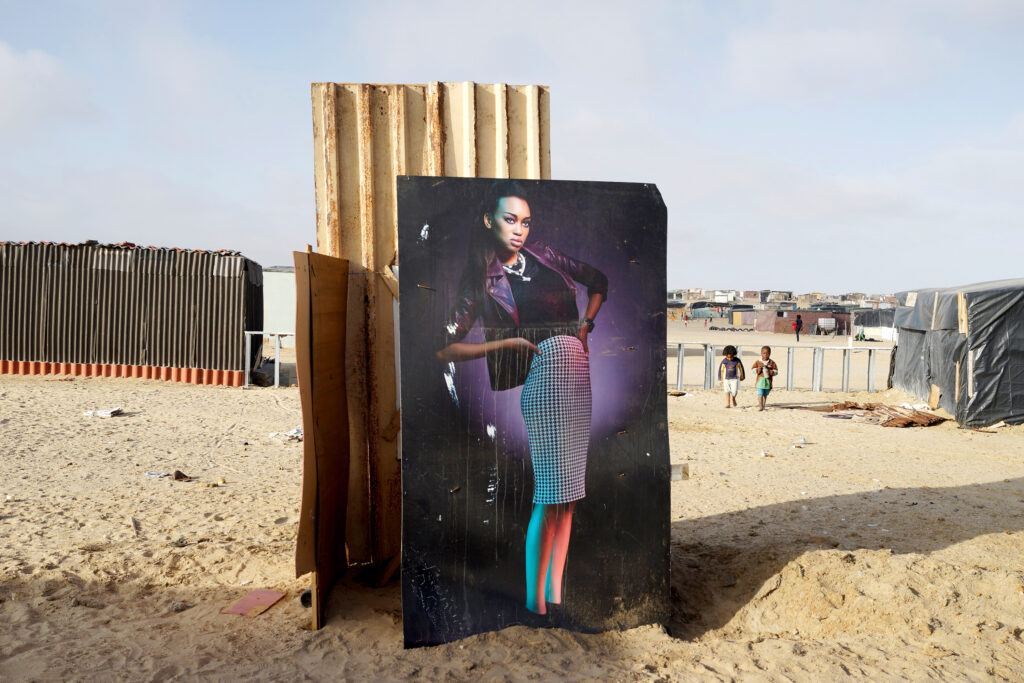
Every day, Natalia Shaanika, 15, escorts her five younger siblings across a busy road to a landfill site to relieve themselves. As they squat – partially hidden by scraps of corrugated iron and used toilet paper – their older sister keeps watch.
When a car comes their way, Shaanika hurries them back half-naked toward their shack. Flies swarm over a bucket of water where they each wash their hands.
“We are a family of eight in a shack in a community that has no water points or toilets,” says Shaanika, who resides in Swakopmund’s Democratic Resettlement Community (DRC), one of Namibia’s largest informal settlements, where some 20,000 people live without running water or sewerage.
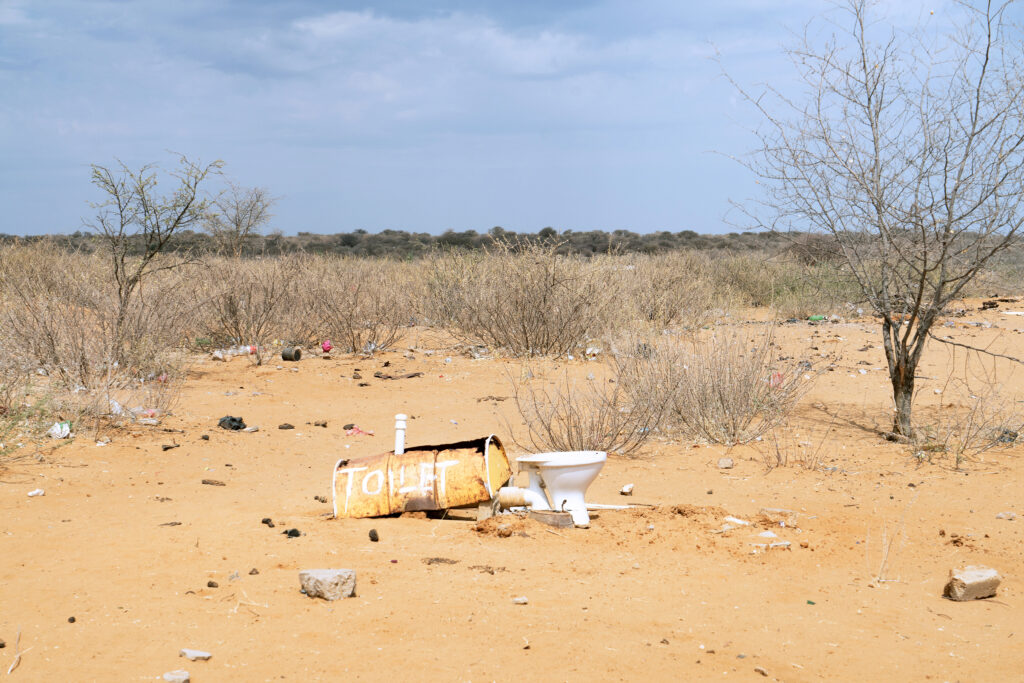

2019 – A toilet in Epukiro Pos-3, a.k.a. ÒThe Lost Place,Ó a bleak encampment in a hostile environment for bushmen who have been evicted from private farms in the Omaheke region of Namibia. This region is the least populous in the country and is largely known today as a place for hunting game by tourists. However, it is also the site of the 20th centuryÕs first genocide, when tens of thousands of Herero and Nama people died at the hands of German forces. Under apartheid rule, they were then removed from their land and placed into camps based on ethnicity. As of 2021, the German government has agreed to pay 1 billion euro over 30 years for projects in communities impacted by the genocide. Up until recently, these groups were excluded from the discussions of German reparations.
These conditions mean Shaanika and her siblings suffer from frequent infections and bouts of diarrhoea, along with the thousands of other men, women and children who use the same and other similar strips of wasteland as toilets in the DRC.
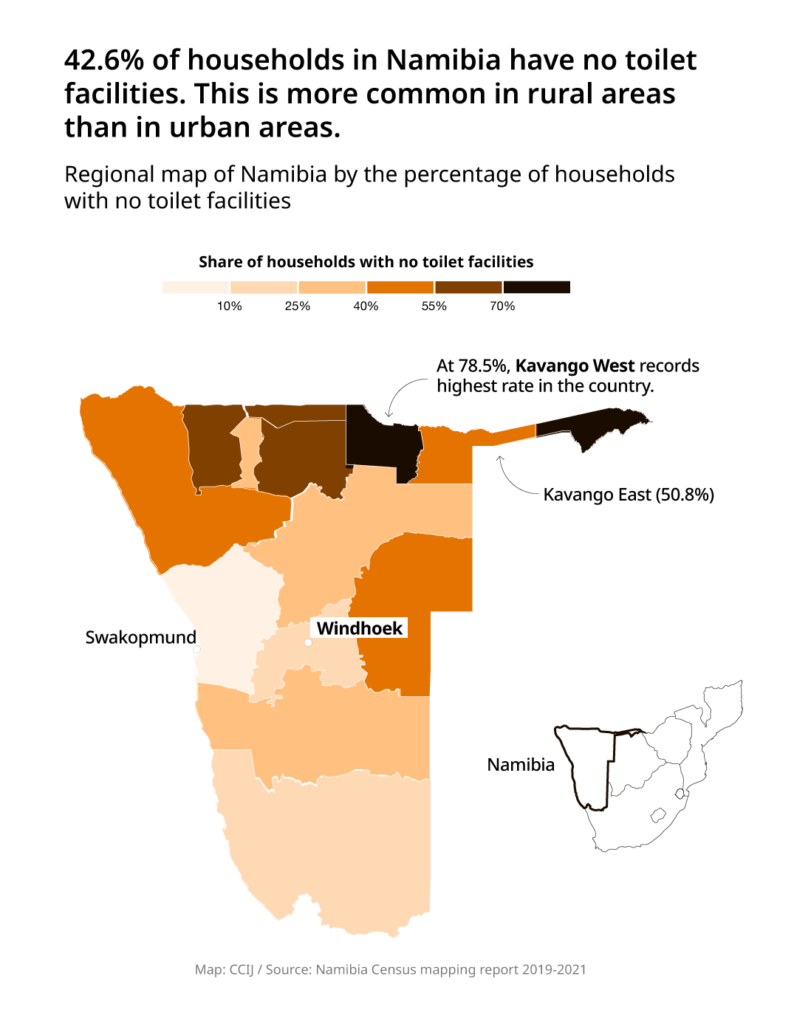
Their struggle is not unique. From the outskirts of cities to the most rural parts of the country, over 1 million Namibians lack adequate access to toilets, and they are often faced with only one option: open defecation.
According to the World Health Organization and UNICEF’s Joint Monitoring Programme (JMP) 2020 data, Namibia ranks sixth for the highest rates of open defecation in the world at 47%. Less than half of the country’s 2.5 million citizens use facilities that safely separate waste from human contact, while some 5% use inadequate facilities such as open pits, buckets and hanging latrines.
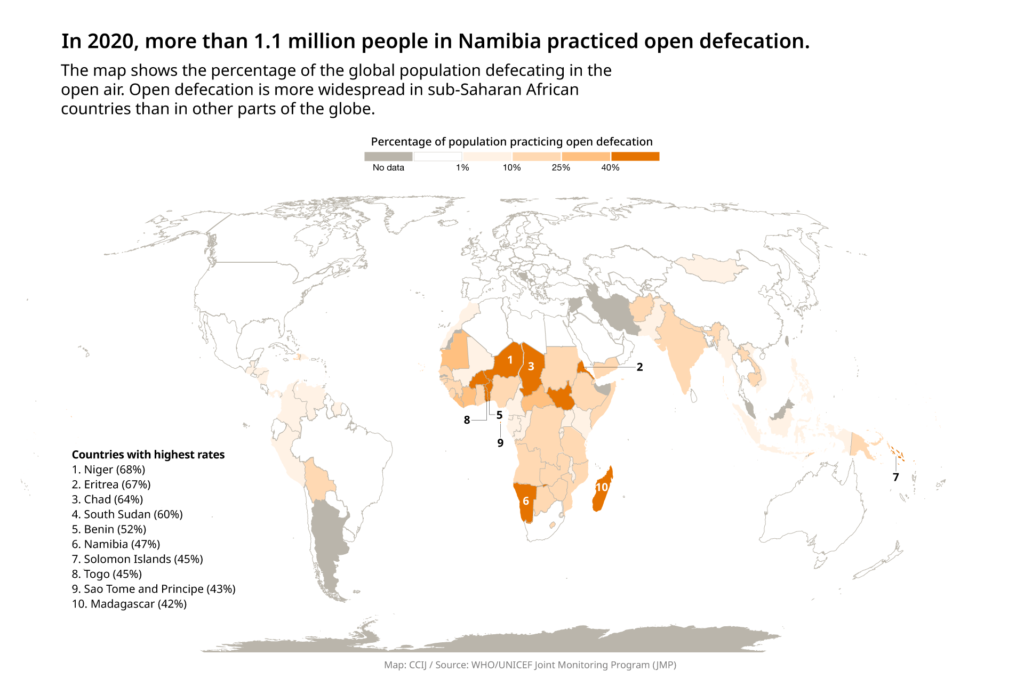
The nation’s severely low levels of sanitation stand in stark contrast to the rest of southern Africa, a region where Namibia ranks the worst for sanitation coverage. Its rates of open defecation are more than double Angola’s to the north and almost five times higher than that of either neighboring Botswana or Zambia.
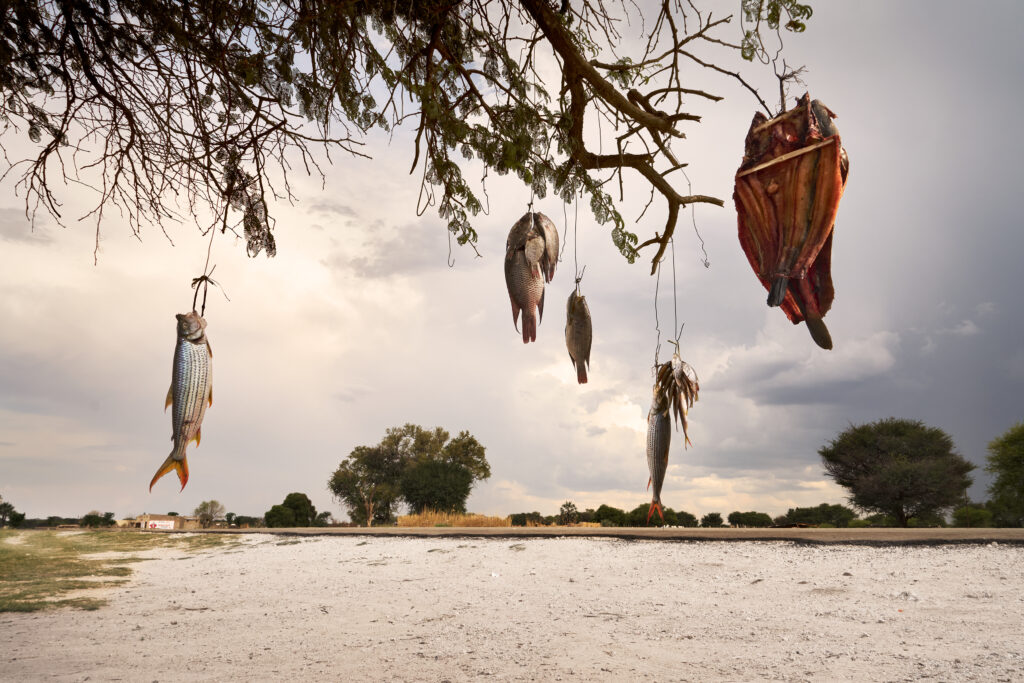
The consequences extend far beyond foul odor. The sheer amount of human feces deposited in and around Namibian homes makes avoiding contact and even ingestion almost impossible. Excrement litters the ground in spaces between shacks where children play with dirty hands, and flies travel freely from waste to fluids and food. As feces seep into the environment, crops are contaminated alongside vital water sources used for drinking, cooking and fishing.
These conditions put Namibians, especially children, at risk of deadly fecal-oral diseases and infections that cause diarrhoea, the second biggest killer of under-fives in the country, while sanitation-related deficiencies such as malnutrition and stunted growth are also prevalent.
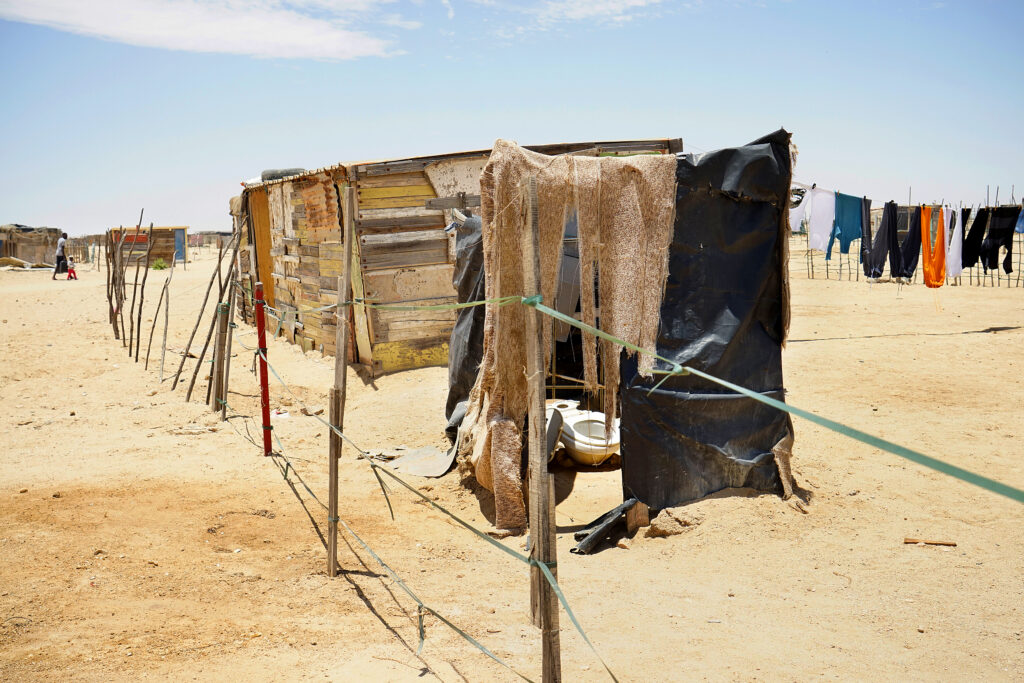

2022 – A typical homemade toilet in the Democratic Resettlement Camp outside of Swakopmund, Namibia.
“If we don’t change our trajectory, things are definitely going to get worse, especially in the informal settlements and in the rural areas,” said Matheus Shuuya, water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) specialist at UNICEF Namibia. “We will experience more children getting sick… I’m sure we will also experience frequent outbreaks of other diseases.”
Education, dignity and safety are in jeopardy, too. Girls’ inability to manage their menstrual health on school premises that lack adequate sanitation leads to increased absenteeism, while Namibians risk rape, robberies and even wildlife attacks as they are forced to seek the privacy of the bush.
Reinard Enrich, 18, was attacked at night while defecating on a landfill in Havana, an informal settlement outside of Windhoek, the nation’s capital. “The absence of toilets has made our situation unsafe,” he said. “I was minding my own business, playing music on my phone. Two men approached me – one grabbed me by my throat, and another grabbed my phone. I couldn’t do anything, so I do not go out when it’s dark anymore.”
However, Namibia has ratified the core international human rights treaties which protect the right to sanitation, while its own constitution calls for “consistent planning to raise and maintain an acceptable level of nutrition and standard of living of the Namibian people and to improve public health.”
Namibia’s 2008 Water and Sanitation Supply Policy outlines that “essential water supply and sanitation services should become available to all Namibians, and should be acceptable and accessible at a cost which is affordable to the country as a whole.” The South West Africa People’s Organization (SWAPO) Party, which has governed the country since independence in 1990, has also committed Namibia to the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goal Six (SDG6) of ensuring all of its citizens have access to clean water and sanitation by 2030.
But according to JMP data, analyzed by the Center for Collaborative Investigative Journalism (CCIJ), stagnant sanitation levels over the past decade mean Namibia is not on course to hit these targets – not even close. While over 1 million Namibians wait for this basic human right to be granted, the government appears to be taking too few steps to address a crisis that may yet worsen due to climate change and rapid urbanization.
Despite pouring billions of Namibian dollars into sanitation in recent years, the country’s 5th National Development Plan stated that the sanitation sector has suffered from “poor coordination, lack of accountability, and spreading efforts and resources too thinly.” Though the current administration has vowed to improve sanitation access and to invest in educating Namibians on the value of good hygiene, it’s still too early to assess how successful this initiative will be.
Dr. Kalumbi Shangula, Namibia’s Minister for Health and Social Services, recognized the struggles facing Namibians. He told CCIJ that low sanitation was overburdening health services and keeping Namibians out of work, but he remained optimistic that conditions would improve. “[G]radually [sanitation] will catch up… As long as there is good will and people are talking about strategies, there is hope,” he said.
But many Namibians need more than hope.
Hilma Hamalwa, 35, lives a 30-minute walk from Shaanika in the DRC. When she realized that her neighbors were suffering from the same infections and illnesses after using the bush to defecate, she dug a hole in the ground for them — and added four slabs of corrugated iron for a little privacy.
“This is not the kind of life a human being should live,” she says.
Editorial: Yaffa Fredrick, Ajibola Amzat
Data: Sotiris Sidieris, Yuxi Wang
Design and visuals: Jillian Dudziak and Scott Lewis